Hyperpigmentation is one of the most common skin concerns—but it’s also one of the most misunderstood and stubborn to treat. Whether you’re dealing with dark spots from acne, sun damage, or melasma, the key to fading discoloration lies in knowing what actually works and how to use it effectively.
In this guide, we’ll cover:
- What hyperpigmentation is
- Types and causes
- Ingredients and treatments that really work
- Prevention strategies
- A skincare routine to help fade discoloration over time
What Is Hyperpigmentation?
Hyperpigmentation refers to darkened patches or spots on the skin caused by an overproduction of melanin (the pigment that gives your skin its color).
It can appear anywhere on the body but is most common on the face, neck, hands, and décolletage.
What Causes Hyperpigmentation?
There are several types of hyperpigmentation, each with different triggers:
1. Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH)
- Triggered by inflammation (e.g., acne, eczema, cuts, or burns)
- Common in medium to darker skin tones
2. Sunspots (Solar Lentigines)
- Caused by UV exposure over time
- Appear as brown spots on sun-exposed areas
3. Melasma
- Often triggered by hormonal changes (e.g., pregnancy, birth control)
- Appears as symmetrical brown patches, especially on cheeks and forehead
4. Freckles
- Genetic but can darken with sun exposure
Ingredients That Actually Work for Hyperpigmentation
Here are the most effective, research-backed ingredients to help fade dark spots and even out your skin tone:
1. Vitamin C
- Brightens skin and inhibits melanin production
- Also provides antioxidant protection
Look for: L-ascorbic acid (10–20%), paired with vitamin E and ferulic acid
Use in the morning under sunscreen
2. Niacinamide (Vitamin B3)
- Reduces inflammation and pigment transfer
- Suitable for sensitive skin
Ideal for: Reducing post-acne marks and overall tone correction
Use morning or night, safe with most other actives
3. Alpha Arbutin
- A gentle melanin inhibitor derived from hydroquinone
- Effective and safe for long-term use
Best for: All skin types, especially sensitive skin
Use twice daily for best results
4. Azelaic Acid
- Brightens skin, calms inflammation, and treats acne
- Great for PIH and rosacea-prone skin
Concentration: 10–20%
Use daily, can be layered under moisturizer
5. Tranexamic Acid
- Blocks pathways that lead to excess melanin
- Especially effective for melasma
Found in serums and creams, often combined with other actives
6. Exfoliating Acids (AHAs/BHAs)
- Glycolic acid helps remove dead skin cells and improves product penetration
- Lactic acid is gentler but still effective
- Salicylic acid is ideal for acne-prone skin
🕒 Use 2–3x per week at night (start slow to avoid irritation)
7. Retinoids (Retinol, Tretinoin)
- Increases cell turnover, fades dark spots, and boosts collagen
- Also helps reduce fine lines and acne
Start with over-the-counter retinol, then progress to prescription if needed
Always use sunscreen with retinoids as they increase sun sensitivity
8. Hydroquinone (2–4%)
- The gold standard for stubborn hyperpigmentation
- Can be used short-term under dermatological guidance
Should be cycled (e.g., 3 months on, 3 months off) to prevent rebound pigmentation
The Most Important Step: SUNSCREEN
No matter what treatment you use, nothing works if you skip SPF.
Why?
- UV exposure worsens hyperpigmentation
- Even visible light can darken spots
Use:
- Broad-spectrum SPF 30+ or 50+
- Every single day—even indoors or on cloudy days
- Reapply every 2 hours if outdoors
Look for tinted mineral sunscreens for added protection against visible light
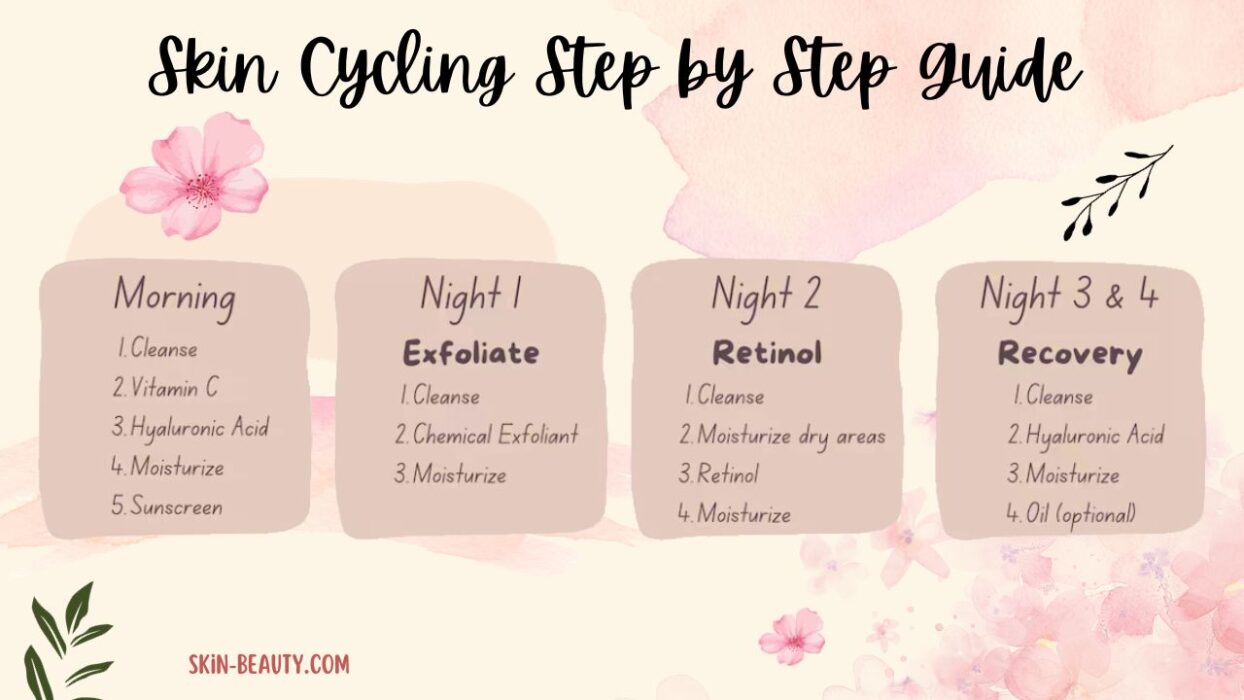
Suggested Skincare Routine for Hyperpigmentation
Morning:
- Gentle cleanser
- Vitamin C serum
- Niacinamide or alpha arbutin serum
- Moisturizer
- Broad-spectrum SPF 50
Night:
- Cleanser
- Chemical exfoliant (2–3x/week) or azelaic acid
- Retinol or targeted serum (e.g., tranexamic acid)
- Moisturizer (with ceramides or peptides)
What to Avoid
- Harsh scrubs or DIY remedies like lemon juice (can damage skin)
- Overuse of actives (can cause irritation and worsen pigmentation)
- Skipping sunscreen (undermines all progress)
Additional Tips
- Be patient—results can take 8–12 weeks or more
- Take before and after photos to track progress
- Use products consistently and stick to a routine
- Don’t mix too many actives without professional advice
- Consider in-office treatments (peels, microneedling, lasers) for faster results
When to See a Dermatologist
If you’re not seeing improvement after 3–4 months of over-the-counter products or you have severe melasma or scarring, it’s time to consult a dermatologist. They can:
- Prescribe stronger treatments (e.g., tretinoin, hydroquinone)
- Recommend in-office procedures like chemical peels or laser therapy
Summary: What Actually Works for Hyperpigmentation
| Ingredient | Benefits | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin C | Brightens, antioxidant | Use AM under SPF |
| Niacinamide | Reduces inflammation & pigmentation | Good for all skin types |
| Alpha Arbutin | Lightens dark spots gently | Use twice daily |
| Azelaic Acid | Calms and fades PIH | Ideal for rosacea/acne |
| Tranexamic Acid | Targets melasma | Use with vitamin C or niacinamide |
| AHAs/BHAs | Exfoliate and brighten | Use 2–3x/week |
| Retinoids | Boost cell turnover | Use at night |
| Hydroquinone | Potent pigment corrector | Use short term under supervision |
| SPF | Prevents and protects | Use daily and reapply |
Final Thoughts
Hyperpigmentation is a complex but treatable condition. The key is using the right ingredients consistently, avoiding triggers, and protecting your skin from UV rays.
There’s no one-size-fits-all solution—but with a targeted, gentle, and consistent approach, you can achieve brighter, more even-toned skin.